Abstract
Text-to-video (T2V) models have recently undergone rapid and substantial advancements. Nevertheless, due to limitations in data and computational resources, achieving efficient generation of long videos with rich motion dynamics remains a significant challenge. To generate high-quality, dynamic, and temporally consistent long videos, this paper presents ARLON, a novel framework that boosts diffusion Transformers with autoregressive (AR) models for long (LON) video generation, by integrating the coarse spatial and long-range temporal information provided by the AR model to guide the DiT model effectively. Specifically, ARLON incorporates several key innovations: 1) A latent Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder (VQ-VAE) compresses the input latent space of the DiT model into compact and highly quantized visual tokens, bridging the AR and DiT models and balancing the learning complexity and information density; 2) An adaptive norm-based semantic injection module integrates the coarse discrete visual units from the AR model into the DiT model, ensuring effective guidance during video generation; 3) To enhance the tolerance capability of noise introduced from the AR inference, the DiT model is trained with coarser visual latent tokens incorporated with an uncertainty sampling module. Experimental results demonstrate that ARLON significantly outperforms the baseline OpenSora-V1.2 on eight out of eleven metrics selected from VBench, with notable improvements in dynamic degree and aesthetic quality, while delivering competitive results on the remaining three and simultaneously accelerating the generation process. In addition, ARLON achieves state-of-the-art performance in long video generation, outperforming other open-source models in this domain. Detailed analyses of the improvements in inference efficiency are presented, alongside a practical application that demonstrates the generation of long videos using progressive text prompts.
Method
Our method first generates long-term, coarse-grained discrete visual units (AR codes) autoregressively using a decoder-only Transformer. These discrete AR codes are then segmented and sequentially fed into the DiT model by the proposed semantic injection module, which autoregressively generates high-quality video segments.
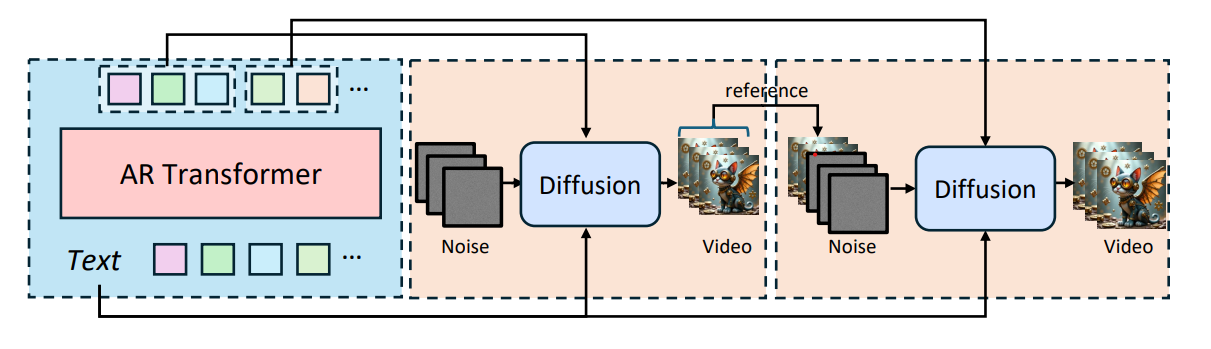
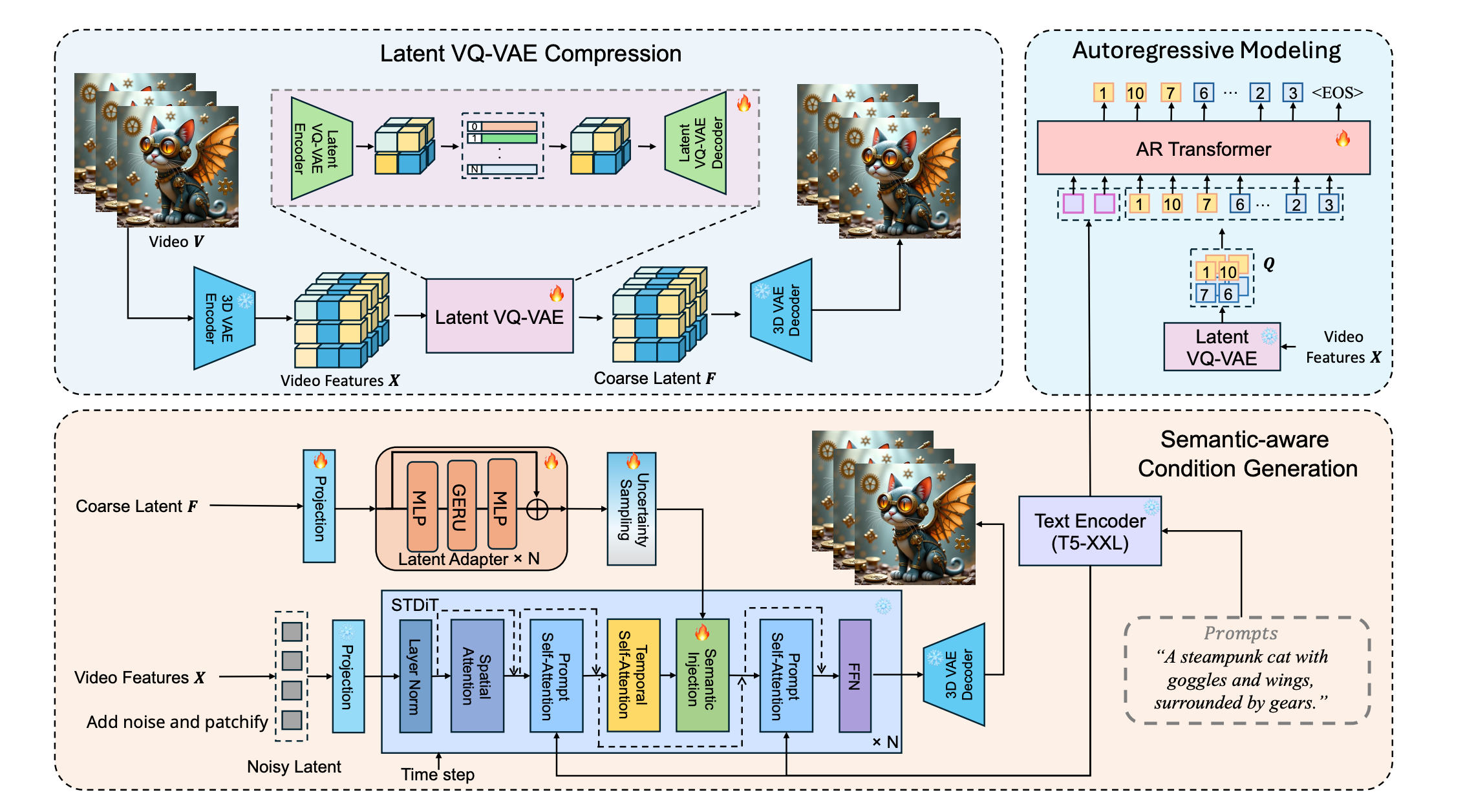
Given a text prompt, the autoregressive (AR) model predicts coarse visual latent tokens, which are constructed from a 3D VAE encoder followed by a latent VQ-VAE encoder based on the target video. These predicted visual latent tokens encapsulate both the coarse spatial information and consistent semantic information. Based on these tokens, a latent VQ-VAE decoder generates continuous latent features, which serve as semantic conditions to guide the DiT model with a semantic injection module. To mitigate the noise inevitably introduced during AR inference, we introduce two noise-robust training strategies: 1) coarser visual latent tokens, and 2) uncertainty sampling module.
Long Video Results
"A teddy bear is swimming in the ocean."
"In a mesmerizing underwater world, vibrant coral reefs teem with life, their colors ranging from deep purples to bright oranges. Schools of tropical fish, including angelfish, clownfish, and tangs, dart gracefully through the water, their scales shimmering in the filtered sunlight"
Text-to-Video Results
"A high-quality 3D render of a female character with curly blonde hair and striking blue eyes, wearing a black tank top, standing before a dramatic, fiery backdrop, with a serious expression and detailed, realistic lighting."
"A cute happy Corgi playing in park, sunset"
"A tranquil coastal beach in spring with golden sands and lush green cliffs is suddenly disrupted by intense shaking, turning rhythmic waves chaotic, creating a surreal visual experience"
"Misty mountains at sunrise, with the sun casting a warm glow. Dense fog adds mystery, while a calm river winds through the scene. Cool colors contrast with the warm light. The video focuses on the untouched natural beauty, free of text or human activity."
Progressive Prompts Results
Prompt1: "A majestic dormant volcano rises in the center of a tranquil landscape, with its rugged slopes contrasting the lush forest below, set against clear skies and rolling hills, evoking a sense of solitude and timeless serenity."
Prompt2: "An erupting volcano dominates the scene, with fiery lava and ash contrasting the lush forest below, as dark clouds and lightning fill the sky, capturing the chaos and power of nature's fury"
Video Condition Generation of ARLON
"A bearded man with short hair, wearing sunglasses and a black leather jacket with red lining, looks upwards seriously in a close-up portrait against a green-to-blue gradient background, suggesting nighttime."
"A high-quality 3D render of a female character with curly blonde hair and striking blue eyes, wearing a black tank top, standing before a dramatic, fiery backdrop, with a serious expression and detailed, realistic lighting."


